The new data protection law will incorporate a new figure that, although it will not be mandatory, will be fundamental for the fulfillment of the new obligations to be complied with in relation to this matter.
Learn how the new Data Protection Law addresses this new charge and how organizations can benefit from it.
Law 19,628 v/s New Data Protection Law
The incorporation of a Data Protection Officer (DPO) represents a drastic change in the legislation:
| Law 19,628 | Data Protection Bill |
|---|---|
| 1) Ley 19.628 does not refer to this figure. 2) Law 20,575, which establishes the Principle of Purpose in the Processing of Personal Data, establishes that distributors of databases of an economic, financial, banking or commercial nature, must designate a natural person so that the data subjects can contact him/her. | It is a requirement to have a DPO within the Infringement Prevention Models. |
What is a DPO?
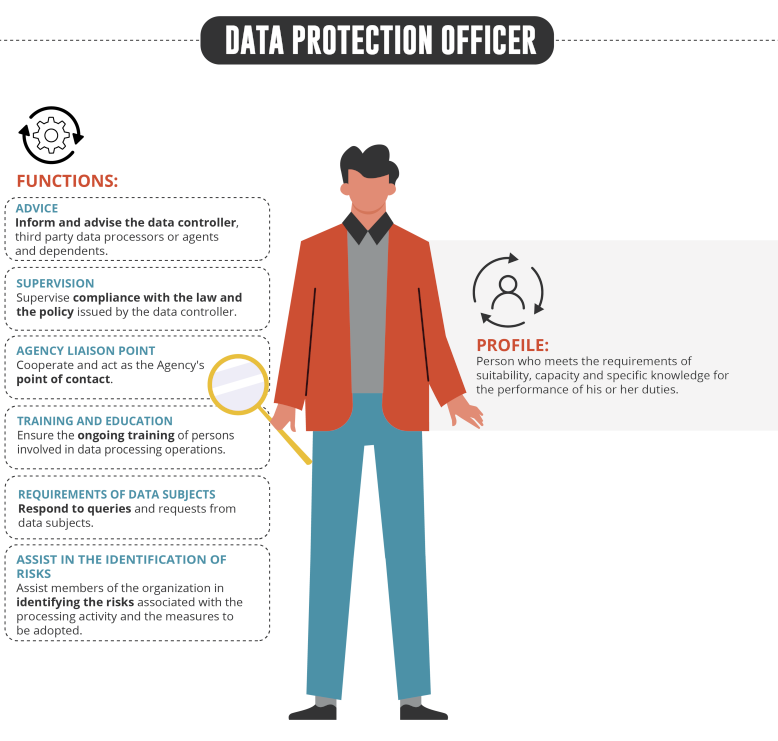
The Data Protection Officer, also known as “DPO”, is who fulfills the function of informing and advising the data controller (as well as the third-party processors, agents and employees of the controller) regarding the compliance with the data protection regulation.
The new law does not oblige controllers to have a data protection officer, but it does expressly regulate this position as an essential part of the adoption of a voluntary infringement prevention model, which results in some benefits for the controller (e.g. mitigating liability).
Under this regulation, the appointment of the DPO must be the responsibility of the highest managerial or administrative body of the organization, which must ensure that it is granted sufficient autonomy and resources to carry out its duty.
What are the duties of the Data Protection Officer?
In addition to informing and advising the data controller, third party data processors, and employees of the controller, the DPO has the task of promoting the policy dictated by the data controller regarding the protection and processing of personal data, as well as supervising compliance with the law and be in charge of the permanent training of the people involved in data processing activities.
In the performance of its duties, the DPO must assist the members of the respective organizations in identifying the risks associated with the processing activity and the measures to be adopted to protect the rights of the data subjects, as well as developing an annual work plan and be accountable for its results. It is the DPO who the data subject can contact, as a first point of contact, with any query or request regarding their rights regarding the protection of personal data.
Finally, the DPO works as a point of connection between the respective organization for which he/she deploys his/her duties and the Personal Data Agency.
Benefits of having a DPO in the organization
Having a DPO, in addition to the multiple benefits associated with comprehensive compliance with personal data legislation within each organization, is associated with an important consequence under the new Data Protection Law.
Indeed, it is considered as a mitigating circumstance of responsibility to have diligently fulfilled the duties of direction and supervision of the infringement prevention models certified by the Data Protection Agency; and given that the DPO is an essential part of the Prevention Model, its appointment is essential against potential infringement infractions when determining the amount of fines.
Prevention Officer or Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- Supervises compliance with the law and the policy dictated by the controller, among other functions.
- Appointed by the highest managerial or administrative authority of the controller (board of directors, managing partner or highest authority of the company). It may perform other duties, to the extent it is ensured that it does not create any conflict of interest.
- Business groups can appoint a single DPO for the same group of companies and entities.
- It has autonomy with respect to the administration in matters related to the law and must be granted the means, faculties and material resources necessary for the performance of its duties.
- Appointment of the DPO must fall on a person who meets requirements of suitability, capacity and specific knowledge.