One of the main critics to Law 19,628 has been the absence of an administrative body to ensure compliance.
Find out how the new Data Protection Law establishes the new supervisory authority that will be in charge of monitoring compliance and sanctioning eventual infringements.
Law No. 19,628 v/s New Data Protection Law
The establishment of a supervisory authority, with oversight, regulatory and sanctioning powers is widely considered one of the most important changes to be introduced by the new data protection law.
| Law 19,628 | Data Protection Bill |
|---|---|
| There is no centralized supervisory authority. Control is exercised in a diffuse manner by the courts of justice, the Transparency Council, and the Consumer Protection Bureau (SERNAC). | The Data Protection Agency will be the supervisory authority. |
New supervisory authority
The Data Protection Agency will be the new supervisory authority in personal data protection matters. It is an anthonomus public corporation, of a technical and decentralized nature, with its own legal personality and its own assets, that will be related to the President of the Republic through the Ministry of Economy, Development and Tourism.
The top Management of the Agency will correspond to a Directive Council, composed of three counselors, appointed by the President of the Republic, with the agreement of the Senate, adopted by 2/3 of its members in office.
The purpose of the Agency will be to ensure the effective protection of the rights that guarantee the private life of individuals and their personal data, and to supervise compliance with the law. In addition, it may act either ex officio or at the request of a party.
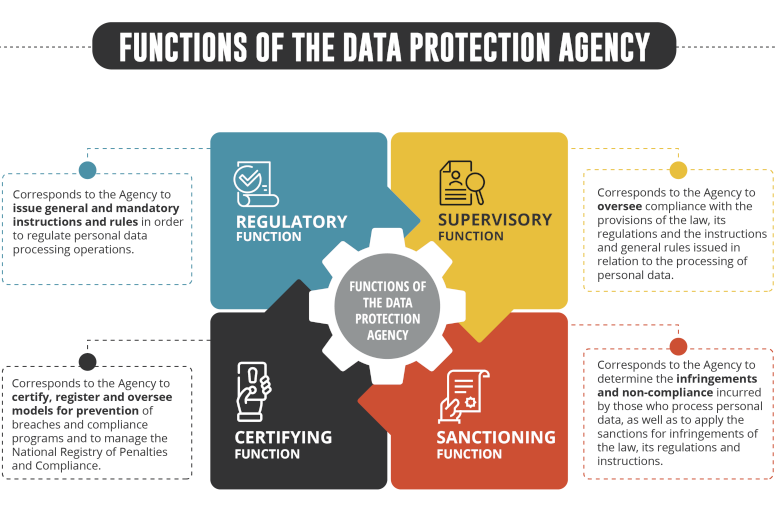
What are its functions and attributions?
The Agency has a variety of attributions, among which are:
- To issue general and mandatory instructions and rules for the purpose of regulating personal data processing operations.
- To apply and administratively interpret the legal and regulatory provisions on the protection of personal data and the instructions and teneral rules issued by the Agency.
- To supervise compliance with the provisions of the law, its regulations and instructions issued by the Agency.
- To determine the infractions and non-compliances incurred by those who carry out the processing of personal data.
- It may impose sanctions on natural persons or legal entities who process personal data in non-compliance with the law, its regulations or general rules issued by the Agency.
- To certify, register and supervise the infringement prevention models and compliance programs.
- To administer the National Register of Sanctions and Compliance.