What is a personal data impact assessment (PDPIA) and when does it need to be carried out?
Find out how the new Data Protection Law integrates this new mechanism of risk analysis against risky personal data processing and the cases in which it is mandatory to perform it.
law No. 19,628 v/s New Data Protection Law
The obligation for data controllers to carry out PDIA is another of the major new features to be introduced by the new Data Protection Law.
| Law 19,628 | Data Protection Bill |
|---|---|
| There is no obligation to conduct PDPIA. | Mandatory PDPIA for certain types of data processing. |
What is a Personal Data Protection Impact Assessment?
A PDPIA is a risk analysis of a given project involving the processing of personal data, with the purpose of assessing possible harm to the rights of data subjects. Once the analysis has been carried out, a report is issued to identify the risks (threats) and determine what measures need to be taken, either to eliminate or minimize them.
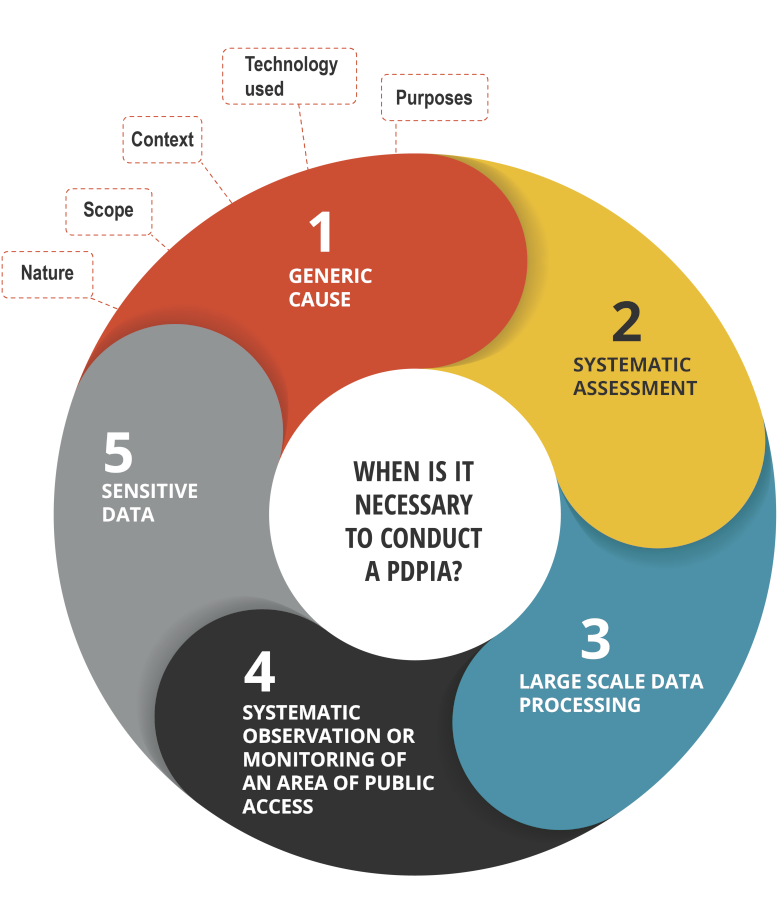
When is it necessary to conduct a PDPIA?
It is not always necessary for the data controller to carry out a PDPIA. However, carrying them out on a voluntary basis when there is no legal obligation is always beneficial for the organization, since it will be able to detect risks and will represent a proactive attitude of the data controller before the Data Protection Agency.
The new Data Protection Lawsets forth two situations in which it is mandatory to carry out this assessment:
- Generic cause: When it is likely that a type of data processing by its (i) nature, (ii) scope, (iii) context, (iv) technology used or (v) purposes, may produce a high risk to the rights of data subjects, the data controller must carry out, prior to the start of the processing operations, a personal data protection impact assessment.
- Specific causes:
- Systematic evaluation of personal data, such as profiling.Large-scale processing of personal data.
- Processing involving systematic observation or monitoring of publicly accessible areas.
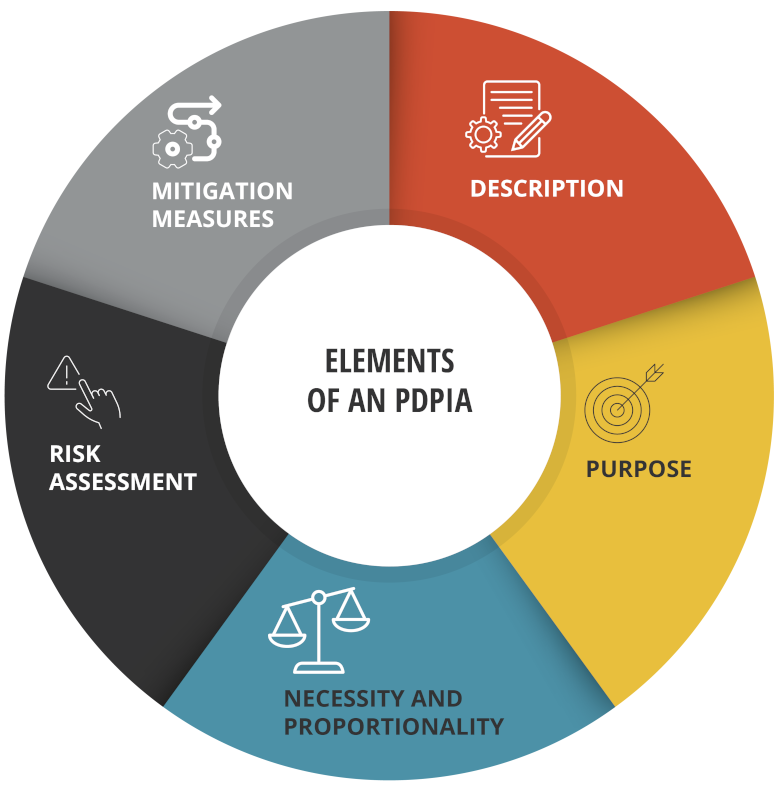
Which element must the PDPIA contain?
According to the new law, the Agency will be responsible for establishing minimum guidelines for this evaluation.
These should include, at least:
- Description of the processing operations.
- Purpose of the processing operations.
- Assessment of the necessity and proportionality of the processing operations with respect to its purpose.
- Risk assessment.
- Mitigation measures.