What are the principles of personal data processing and which are they? Why are they important?
Find out how the new Data Protection Law sets forth principles that must be considered in each activity that involves the processing of personal data.
Current regulatory context v/s Data Protection Bill
The new Data Protection Law contrasts with Law 19,628 in the way it addresses the principles of personal data processing.
| Law 19.628 | Draft Law on Personal Data |
|---|---|
| It does not contain explicit guiding principles. They are built on various standards. | It contains guiding principles delimited by Article 3. Failure to comply with the principles constitutes a violation in terms of the law. |
Principles in the Bill
The principles of data processing regulate the way in which controllers and processors must process personal data.
It is the duty of data controllers to comply with the principles established by the new law. In this sense, they are not mere voluntary guidelines, but real obligations. This idea is reinforced by article 33 of the new law, which provides that the person responsible shall be punished for violating the principles set forth in article 3.
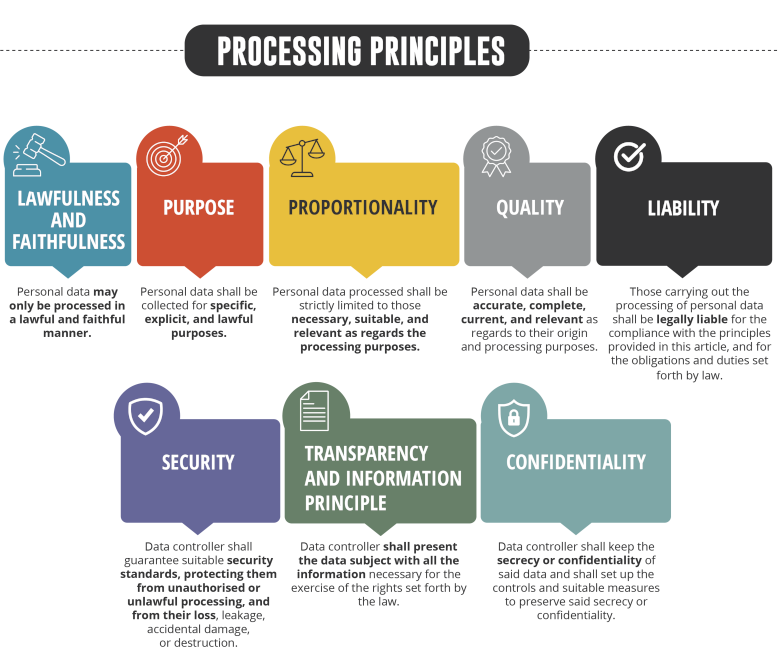
Lawfulness and faithfulness
The data controllers may only process data in a lawful and faithful manner (that is, only if they are empowered by some source of legality to do so), and with fidelity to the purposes that the corresponding legal basis allows them.
Purpose
Personal data must be collected for specific, explicit and lawful purposes, hence personal data cannot be processed for purposes other than those informed at the time of collection. The foregoing with the exceptions of special cases, such as when consent is agreed again, when it is provided by law or other specific cases.
Proportionality
The personal data processed can only be those that are necessary, appropiate and relevant in relation to the purposes of the treatment.
Quality
The personal data processed must be accurate, complete, current and relevant in relation to their origin and the purposes of the processing.
Liability
Those who process personal data will be legally responsible for compliance with the principles, obligations and duties contained in the law.
Security
Controllers must ensure adequate security standards, protecting data against unauthorized or unlawful processing, establishing appropriate security measures (security principle).
Transparency and information
The data subject must be given all the necessary information for the exercise of the rights established by the law.
Confidentiality
Data controllers and those who have access to personal data must keep secrecy or confidentiality about them, and must establish controls and appropriate measures for this purpose.
Importance of principles throughout the Bill
The Agency shall issue instructions and mandatory general rules to regulate the processing of personal data in accordance with the principles indicated in the law.
Failure to comply with these principles constitutes an infringement, which, depending on its seriousness, can be classified as minor, serious and very serious.